LED Backhaul Project Engineer Blog
Let's use our own 3D printer: Stereolithography method
Last Update: October 26th, 2021
Introduction
While 3D printers that use heat to melt the base material, such as the FDM and SLS methods, are similar in that the layers are formed one at a time, the stereolithography method uses UV light to irradiate liquid resin (commonly known as resin) that hardens with UV light.
In a previous article, I described the fabrication of parts using a 3D printer that uses the FDM/FFF method. In this article, I will describe the characteristics of the stereolithography 3D printer and how it is different from the FDM method.
3D printer stereolithography method
In the FDM and SLS methods, the molding table faces upward, and molding proceeds by building up one layer at a time. In the stereolithography method, the fabrication table faces downward, and fabrication proceeds by hanging down one layer at a time. The molding direction is upside down, but they are completely the same in that the molding is done in order from the bottom of the prepared 3D data.
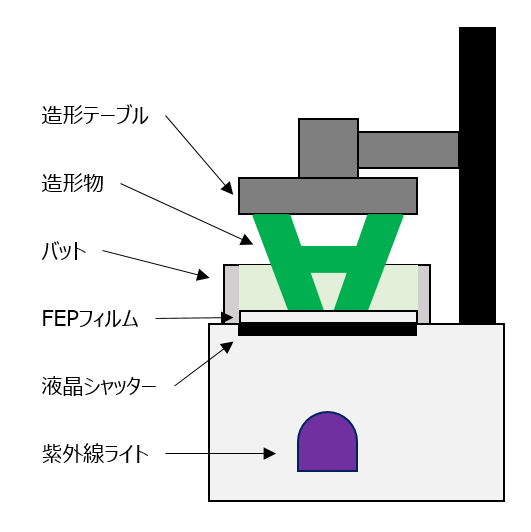
The general structure of an award-winning 3D printer consists of, in order from the bottom, a UV light, an LCD shutter, a bat (a tank for storing resin), and a molding table. (There are also products that use an array of ultra-small mirrors in place of the liquid crystal shutter, but these are not included in this article.)
[Figure 1:Structure of a stereolithography 3D printer]
A transparent FEP film is attached to the bottom of the bat, which serves as a light window to supply UV light to the resin, and the resin is hardened by irradiating the bat with UV light from below. LCD shutters are used to select the areas to be sculpted or not to be sculpted on the molding table. When the LCD shutters are open, UV light can pass through, so the part is sculpted, and when they are closed, UV light cannot pass through, so the part is not sculpted.
Since the resolution of the object in the vertical and horizontal directions depends on the resolution of the liquid crystal shutter, it can be formed with a much smaller error than the FDM method, which uses a motor and a rail or belt to physically move the nozzle. However, unlike the FDM method where the upper and lower layers do not assimilate due to the gradual cooling immediately after being ejected from the nozzle, the optical fabrication method assimilates the upper and lower layers so that the stacking marks that are characteristic of 3D printers are not noticeable and the strength of the product does not deteriorate in the stacking direction. In addition, it is isotropic in terms of strength and does not easily peel off in the stacking direction (FDM is anisotropic in that it easily peels off in the stacking direction).
On the other hand, there is a wide range of thermoplastic resins used in FDM, and it is possible to change the physical properties by using fillers (additives such as glass, carbon fiber, wood chips, etc.), but the resins used in stereolithography are mainly hard and brittle, so they are inferior to FDM in terms of simple strength. It is possible to use a resin with improved strength for models costing several hundred thousand yen or more, but I have never used it, so I cannot mention it.
How to handle modeling objects
It is no different from the FDM method in that the 3D data designed by 3D CAD software is output as STL files and converted into data that is sent to the 3D printer by slicing software. Since the irradiation time required for curing differs depending on the model and individuality of the 3D printer, the manufacturer of the resin, and the color of the resin, it is important to test print and determine the required number of seconds before starting the actual fabrication. Before starting the actual molding process, make a test print to determine the required number of seconds.
Prolonged exposure ensures curing, but the cured area may spread out more than necessary, causing the dimensions of the object to increase. On the other hand, if the curing time is too short, the resin will not cure properly and the object will not be formed correctly.
The process is similar to the FDM method in that the data is fed into the 3D printer and watched over as the molding process is completed. However, after the molding process is complete, there is a post-processing step called "cleaning" and "secondary hardening".
Washing means cleaning the object with IPA (isopropyl alcohol) to wash off excess resin clinging to the object. However, there are some resins that cannot be removed by this method alone. Some resins can be washed with tap water, but they have their own problems such as dimensional changes due to moisture absorption and long drying time after washing.
Secondary curing is the process of re-irradiating the material with UV light to harden the material, which is not fully cured when the 3D printer has completed the molding process. Therefore, it is necessary to irradiate the material with sunlight or a separately prepared ultraviolet light to cure it completely. Special equipment for secondary curing is available, but it is also possible to make your own by combining a nail UV light and a turntable.
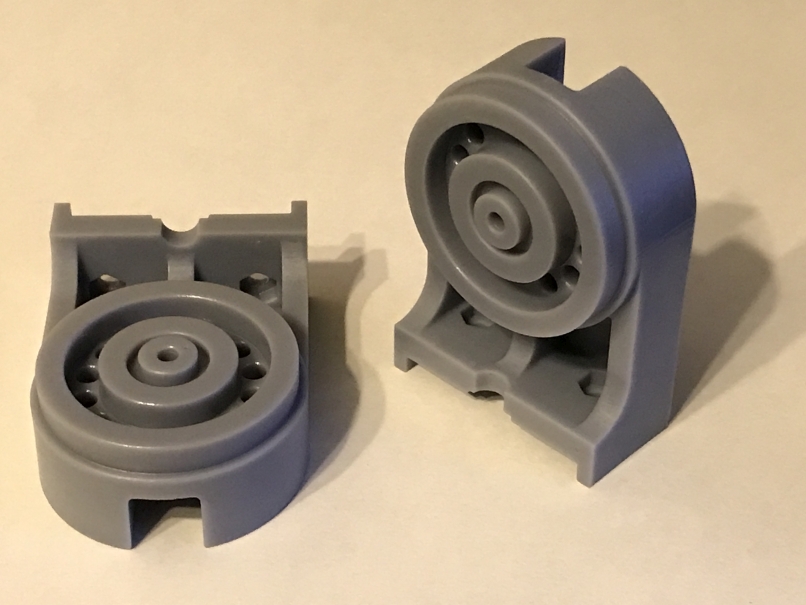
The following is a list of parts that have completed secondary curing that were formed using a stereolithography 3D printer.
[Figure 2:Parts that have completed secondary curing]
Stereolithography method and FDM method
Currently, we can see a variety of products in the low price range of 3D printers under 100,000 yen, both in the stereolithography method and the FDM method. As I have often compared them in this article, my personal opinion about these two methods, which one should be introduced and which one is superior, is that it would be better to introduce the FDM method first to get used to handling 3D printers and 3D CAD, and then introduce the stereolithography method when you are not satisfied with the accuracy of the FDM method. If you are not satisfied with the accuracy of the FDM method, I think it would be a good idea to introduce the stereolithography method.
Both methods have different handling methods and different advantages and disadvantages, so it is impossible to make a simple comparison, but handling liquid resin is quite a hurdle, so I think that the FDM method is appropriate for the first introduction. After that, it would be good to be able to use different methods, such as the stereolithography method if you want to focus on shape reproducibility and accuracy, and the FDM method if you want to focus on physical strength.